Blog

Pregnancy Fitness and Exercises: 6 Must-Do Exercises for Strong, Healthy Moms
Pregnancy Fitness and Exercises: Stay Active, Stay Healthy Exercise and fitness during pregnancy play a vital role in helping expectant mothers navigate the physical and emotional changes that come with this incredible journey. Pregnancy is a beautiful experience—but it also brings a wave of new challenges. One of the most effective ways to manage these changes and support both your health and your baby’s development is through pregnancy-safe fitness and movement. Contrary to outdated myths, staying active during pregnancy isn’t just safe—it’s encouraged by health experts (as long as your doctor hasn’t advised otherwise). With the right approach, exercise can become a powerful tool to reduce stress, ease discomfort, and boost your energy levels throughout each trimester. In this guide, we’ll explore the proven benefits of exercise and fitness during pregnancy, essential safety tips, and the best exercises for expectant moms. Whether you’re in the early weeks or preparing for delivery, this comprehensive guide will help you stay strong, confident, and connected to your changing body. The Positive Power of Exercise Here’s how regular movement can make your pregnancy experience smoother and healthier: 💪 Improves stamina and muscle tone to support your changing body 🌙 Reduces fatigue and improves sleep quality 😊 Elevates mood and reduces stress thanks to endorphins 🧘 Prepares your body for labor and delivery ⚖️ Helps maintain healthy weight gain 🤰 Reduces common pregnancy discomforts like back pain, constipation, and bloating 💓 Supports cardiovascular health for both you and your baby Say No to Unsafe Workouts: Follow These Guidelines Before starting or continuing an exercise routine, keep these important safety tips in mind: Consult your OB-GYN before starting any workout program. Listen to your body – if something feels off, stop and rest. Stay hydrated and avoid overheating. Avoid high-risk or contact sports, heavy lifting, or exercises with a risk of falling. Wear supportive shoes and comfortable, breathable clothing. Warm up and cool down properly to prevent injuries. Top Pregnancy Exercises for a Strong and Radiant You Walking A simple, low-impact way to get your heart rate up. Great for all trimesters and easy to do anywhere. Prenatal Yoga Perfect for flexibility, relaxation, and pelvic floor strength. It also helps with breathing techniques useful for labor. Swimming & Water Aerobics Being in water takes the pressure off your joints and provides full-body toning without strain. Stationary Cycling A safer alternative to outdoor biking that keeps your legs and heart active. Strength Training (with light weights or resistance bands) Helps maintain muscle tone and posture. Focus on bodyweight exercises like squats, lunges, and wall pushups. Pelvic Floor Exercises (Kegels) Strengthens the muscles that support the uterus, bladder, and bowels. Helps with labor and postpartum recovery. Trimester-Specific Exercise Tips First Trimester (Weeks 1–13) Stick to what you’re already used to. Focus on foundational strength and moderate cardio. Be cautious of overheating, especially in hot weather. Second Trimester (Weeks 14–27) As your belly grows, switch to lower-impact moves. Avoid exercises that require lying flat on your back for long. Incorporate balance exercises to counteract your shifting center of gravity. Third Trimester (Weeks 28–40) Emphasize gentle movement, stretching, and breathing. Prioritize pelvic floor work and mobility to prepare for birth. Don’t overexert—fatigue is more common now, and rest is important. The Incredible Benefits of Staying Active for You and Your Baby Physical Health Benefits: Regular exercise during pregnancy greatly improves overall physical health. It enhances blood circulation, which helps reduce common pregnancy issues like leg cramps, swelling, and varicose veins. Staying active also supports healthy weight gain and helps maintain a balanced body mass index (BMI), which can contribute to a smoother pregnancy and delivery. Building strength and endurance through prenatal workouts prepares the body for labor, making it easier to handle physical stress. Additionally, exercise relieves common discomforts such as back pain, bloating, constipation, and pelvic pressure. Strengthening the core and improving posture also help support the growing belly and reduce strain on the lower back. Even sleep quality often improves with consistent movement, helping pregnant women rest better at night. Mental and Emotional Benefits: Exercise is a powerful tool for supporting mental and emotional well-being during pregnancy. Physical activity triggers the release of endorphins—natural mood enhancers that reduce stress, anxiety, and symptoms of depression. Staying active helps regulate emotions and encourages a more positive mindset during a time of rapid physical and hormonal changes. It also combats fatigue by increasing energy levels, which can be particularly helpful during the sluggish first and third trimesters. Many pregnant women also report feeling more confident and empowered when they incorporate exercise into their routine, helping them maintain a strong connection to their changing bodies. Benefits for the Baby: Staying active during pregnancy isn’t just beneficial for the mother—it also supports healthy fetal development. Exercise can improve placental function, which ensures better oxygen and nutrient delivery to the baby. It may also lower the risk of pregnancy-related complications such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and preterm labor. Studies have shown that babies born to mothers who exercise regularly during pregnancy often have healthier birth weights, better cardiovascular function, and higher Apgar scores at birth. These outcomes contribute to a strong start for newborns and may even offer long-term health advantages. Long-Term Benefits: The advantages of prenatal exercise extend well beyond delivery. Women who stay active during pregnancy often experience shorter labor, fewer complications, and quicker recovery times. Strengthening muscles, maintaining flexibility, and building endurance all play a role in preparing the body for childbirth and helping it bounce back more effectively postpartum. Exercise also significantly reduces the risk of postpartum depression by helping stabilize hormones and promoting emotional balance. Lastly, making exercise a routine during pregnancy sets the foundation for long-term wellness. It encourages lifelong healthy habits that can carry into motherhood and inspire a fit and active family lifestyle. Avoid Serious Risks: When It’s Time to Stop Exercising During Pregnancy Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you experience: Vaginal bleeding Dizziness or faintness Chest pain or shortness of breath Calf pain
Fertility & IVF Breakthroughs: 5 Success Rates That Inspire Hope
Fertility and IVF: Transforming Hope into Parenthood For many people, the path to parenthood isn’t always simple. Fertility challenges affect millions of couples worldwide, leading many to explore medical options like IVF (In Vitro Fertilization). Whether you’re just beginning to consider your fertility or are already exploring treatment options, understanding how fertility and IVF work can empower you to make informed decisions on your journey to becoming a parent. In this guide, we’ll break down the basics of fertility, common challenges, and how IVF can offer hope when natural conception proves difficult. Fertility: A Beautiful Beginning to Parenthood Fertility refers to the natural ability to conceive a child. While many couples are able to conceive naturally within the first year of trying, around 1 in 6 couples experience difficulties—a condition referred to as infertility. Key Factors That Affect Fertility: Age: Fertility declines significantly after age 35 in women. Ovulation disorders: Irregular or absent ovulation affects conception chances. Sperm health: Low sperm count or motility can hinder fertilization. Fallopian tube issues: Blockages can prevent egg and sperm from meeting. Endometriosis: Tissue growth outside the uterus can interfere with fertility. Lifestyle: Smoking, alcohol, obesity, and stress all negatively affect fertility. Don’t Ignore the Signs: Seek Help for Infertility . Here are key reasons to consider seeking professional guidance: You’ve Been Trying to Conceive for Over 12 Months (or 6 Months if Over 35) If you’re under 35 and have been trying to conceive for a year without success, it’s a good idea to consult a fertility expert. For those over 35, fertility naturally declines, and waiting too long could reduce the chances of successful treatment. In this case, seeking help after 6 months is recommended to avoid further delays. You Have Irregular or Absent Menstrual Cycles A healthy, regular menstrual cycle is often a sign that ovulation is occurring properly. If your periods are irregular, too long, too short, or completely absent, it may indicate an underlying hormonal imbalance or ovulation disorder. Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), thyroid issues, or early menopause can interfere with ovulation and reduce fertility. You or Your Partner Have a Known Reproductive Health Issue If either partner has a history of reproductive health problems—such as endometriosis, uterine fibroids, low sperm count, or past infections—consulting a specialist early is essential. A fertility expert can conduct thorough evaluations and suggest treatments tailored to your specific situation. You’ve Experienced Multiple Miscarriages Recurrent pregnancy loss, typically defined as two or more consecutive miscarriages, can be emotionally devastating and may signal an underlying medical issue. A fertility specialist can help identify possible causes, such as genetic abnormalities, hormonal imbalances, or autoimmune disorders, and recommend treatment options to improve the chances of a successful pregnancy. IVF: The Powerfull Possibility to Parenthood In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is an assisted reproductive technology (ART) that involves fertilizing an egg outside the body and then implanting the resulting embryo into the uterus. 1. Ovarian Stimulation: The IVF journey begins with ovarian stimulation, a phase designed to boost the ovaries into producing multiple mature eggs instead of the single egg typically released each month. Fertility medications, usually containing follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), are administered daily over a period of 8 to 14 days. During this time, doctors closely monitor the growth of ovarian follicles through regular ultrasounds and blood tests to track hormone levels and ensure the eggs are developing properly. 2. Egg Retrieval: Once the follicles reach the desired size, a “trigger shot” is given to complete the eggs’ maturation. Around 36 hours later, the eggs are retrieved through a minor outpatient procedure called transvaginal ultrasound aspiration. Under light sedation, a thin needle is inserted through the vaginal wall into the ovaries to collect the eggs. This process typically lasts about 20–30 minutes and is followed by a short recovery period. 3. Fertilization Following retrieval, the eggs are taken to the lab where they are fertilized with sperm from a partner or donor. There are two primary methods of fertilization: conventional IVF, where sperm and eggs are mixed together in a dish, and Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), where a single sperm is directly injected into each egg, often used in cases of male infertility. The eggs are then monitored for signs of successful fertilization, which usually occurs within 24 hours. 4. Embryo Culture: Once fertilized, the embryos are placed in an incubator to grow under controlled conditions. Over the next 3 to 5 days, embryologists observe the development of the embryos, watching for cell division and quality. By day 5, embryos may reach the blastocyst stage, a more advanced stage that often leads to better implantation rates. At this point, some clinics offer preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) to check for genetic or chromosomal abnormalities before selection for transfer. 5. Embryo Transfer: One of the healthiest embryos is selected for transfer into the woman’s uterus. This is a painless and quick procedure performed without anesthesia. Using a thin, flexible catheter, the embryo is guided through the cervix and placed directly into the uterine lining. To increase the chances of successful implantation, progesterone supplements are often prescribed to support the endometrial lining during this critical phase. 6. Pregnancy Test: Approximately 9 to 14 days after the embryo transfer, a blood test measuring beta hCG levels is performed to determine whether implantation was successful and pregnancy has begun. A positive test result confirms early pregnancy, while a negative result may lead to discussions about trying another cycle or exploring other fertility options. This final step closes the initial IVF cycle, offering either the joy of a positive result or insight into future reproductive planning. Struggling with Infertility? Here’s Who Can Benefit from IVF IVF is often recommended for individuals or couples facing: Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes Male infertility (low sperm count or quality) Endometriosis Unexplained infertility Ovulation disorders Genetic concerns (via preimplantation genetic testing) Same-sex couples or single individuals using donor sperm or eggs The Hidden Truth: Risks of Fertility Treatments You Must Know”
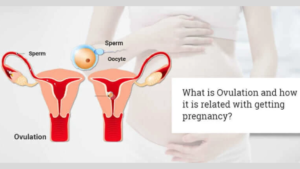
“Conception and Ovulation: 4 Must-Know Tips to Supercharge Your Fertility Tracking
Conception and Ovulation Uncovered: Discover the Power of Your Body Conception and Ovulation is a biological processes form the very beginning of human life—and understanding them can help you make informed choices about your fertility, birth control, or reproductive health. These two of the most fundamental processes in human reproduction, yet they remain widely misunderstood. Whether you’re actively trying to conceive, planning for the future, or simply curious about how your body works, gaining a clear understanding of these natural cycles is a powerful step toward taking control of your reproductive health. Ovulation marks the release of an egg from the ovary—an event that occurs roughly once a month in a healthy menstrual cycle. Conception, on the other hand, happens when that egg is successfully fertilized by a sperm, creating the very first spark of new life. Together, these processes represent the biological starting point of pregnancy and are influenced by a variety of factors including hormones, health conditions, lifestyle choices, and timing. Understanding how ovulation and conception work can empower you to make informed decisions—whether you’re trying to get pregnant, avoid pregnancy, or identify signs of reproductive imbalance. With knowledge comes clarity: knowing when you’re most fertile, how to recognize ovulation, and what might impact your chances of conceiving can all contribute to better outcomes and less stress. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about conception and ovulation—from the science behind your menstrual cycle, to identifying fertile windows, to recognizing when it might be time to seek medical support. Whether you’re on a journey toward parenthood or simply exploring your body’s natural rhythms, this information is here to guide and support you. The Amazing Process of Ovulation Ovulation is the process where a mature egg is released from one of the ovaries. This typically occurs midway through a woman’s menstrual cycle, around day 14 in a 28-day cycle, though it can vary from person to person. Key Stages of Ovulation: Follicular Phase (Days 1–13): Starts with the first day of your period. Hormones stimulate several follicles in the ovaries to grow. One dominant follicle matures and prepares to release an egg. Ovulation (Around Day 14): A surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the ovary to release a mature egg. The egg enters the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized. Luteal Phase (Days 15–28): The ruptured follicle becomes the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone to prepare the uterine lining. If fertilization doesn’t occur, the corpus luteum breaks down, progesterone drops, and menstruation begins. Signs of Ovulation: Mild pelvic or abdominal pain Increased cervical mucus (clear and stretchy) Breast tenderness Slight increase in basal body temperature Surge in LH levels (detectable with ovulation kits) The Miracle of Conception: Where Life Begins Conception is the moment when a sperm successfully fertilizes an egg. This typically occurs within 12–24 hours after ovulation, while the egg is still viable in the fallopian tube. The Journey of Conception: Fertilization: After sexual intercourse, sperm travel through the cervix into the uterus and up into the fallopian tube. If an egg is present, one sperm may penetrate and fertilize it. Zygote Formation: The sperm and egg unite to form a zygote with a complete set of chromosomes (23 from each parent). The zygote begins to divide and travel down the fallopian tube toward the uterus. Implantation: Around 6–10 days after fertilization, the dividing ball of cells (now a blastocyst) implants into the uterine lining. This marks the beginning of pregnancy. Avoiding Missed Chances: How to Track Ovulation for Conception If you’re trying to conceive, timing intercourse around ovulation is crucial. Here’s how to track your fertile window: 1. Calendar Method: Track your cycle for a few months to estimate ovulation day. Best for those with regular menstrual cycles. 2. Basal Body Temperature (BBT): Take your temperature daily before getting out of bed. A slight rise (0.5°F to 1°F) signals ovulation has occurred. 3. Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): Detect LH surge in your urine. A positive result indicates ovulation is likely to occur in the next 12–36 hours. 4. Cervical Mucus Monitoring: Observe your discharge; clear, stretchy mucus signals fertility. Hidden Obstacles That Can Disrupt Ovulation and Conception Age: Fertility declines with age, especially after 35. Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like PCOS can disrupt ovulation. Lifestyle: Stress, weight extremes, smoking, and alcohol can affect fertility. Medical Conditions: Thyroid disorders, diabetes, and certain medications may interfere. Facing Fertility Struggles? Know When to Seek Help If you’re under 35 and haven’t conceived after 12 months of regular, unprotected sex, or over 35 and haven’t conceived after 6 months, it’s recommended to consult a fertility specialist. Irregular cycles, no signs of ovulation, or a known reproductive issue are also reasons to seek medical guidance sooner. Understanding conception and ovulation gives you powerful insight into your reproductive health. Whether you’re planning a pregnancy, preventing one, or simply want to know your body better, tracking your cycle and recognizing the signs of ovulation can make a world of difference. If you’re trying to conceive, remember that timing and health both play key roles—but also give yourself grace. Fertility is a complex journey, and support is always available when you need it. Facebook Youtube Instagram Linkedin
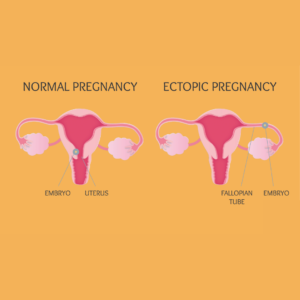
Miscarriage and Ectopic Pregnancy: 10 Life-Changing Facts Every Woman Must Know
Miscarriage and Ectopic Pregnancy: Discover the Courage Within Pregnancy is often a time of hope and excitement, but it can also come with complications and challenges. Two of the most emotionally difficult pregnancy complications are miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy. While they are both forms of pregnancy loss, they differ in cause, symptoms, and treatment. Understanding these conditions can help in recognizing the signs early, seeking the right support, and making informed decisions about care and recovery. Understanding Miscarriage: That Empowers Healing A miscarriage refers to the spontaneous loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week. It’s more common than many realize — affecting around 10% to 20% of known pregnancies. Most miscarriages occur in the first trimester (the first 12 weeks). Common Causes of Miscarriage: Genetic or chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus Hormonal imbalances (such as low progesterone) Maternal health conditions (e.g., diabetes, thyroid issues) Infections Uterine or cervical problems Lifestyle factors (smoking, drug or alcohol use, high caffeine intake) Signs and Symptoms: Vaginal bleeding or spotting Cramping or pain in the lower abdomen Fluid or tissue passing from the vagina Sudden loss of pregnancy symptoms (like nausea or breast tenderness) Ectopic Pregnancy: A Silent Threat You Can’t Ignore An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants and begins to grow outside the uterus — most commonly in a fallopian tube. Unfortunately, an ectopic pregnancy cannot proceed normally and can pose serious health risks if left untreated. Causes and Risk Factors: Previous ectopic pregnancies Inflammation or infection in the fallopian tubes Fertility treatments or IVF Surgery on fallopian tubes or pelvic organs Smoking Signs and Symptoms: Sharp or stabbing abdominal pain (often on one side) Vaginal bleeding Shoulder pain Dizziness or fainting (a sign of internal bleeding, which is a medical emergency) The Truthful Insight: Miscarriage vs. Ectopic Pregnancy Feature Miscarriage Ectopic Pregnancy Location Pregnancy is inside the uterus Pregnancy is outside the uterus (usually fallopian tube) Bleeding Common, can vary in amount Often lighter or irregular Pain Cramping, similar to period pain Sharp, localized pain, may worsen over time Viability Pregnancy is non-viable Pregnancy is non-viable and dangerous to mother Treatment May resolve naturally or need medical/surgical management Requires immediate medical treatment (medication or surgery) Top 10 Hard Truths About Pregnancy Loss You Need to Know 1 in 4 pregnancies may end in miscarriage — and most happen in the first trimester. Ectopic pregnancies affect about 1 in 50 pregnancies — and can be life-threatening if untreated. Miscarriages are rarely caused by something the woman did or didn’t do — guilt is common, but often misplaced. Ectopic pregnancies cannot be carried to term — they require urgent medical attention. Genetic abnormalities are the most common cause of miscarriage — not lifestyle factors. Symptoms of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy can overlap — but localized pain and shoulder pain are red flags for ectopic. Early diagnosis through ultrasound and hCG testing can save lives — especially in ectopic cases. Both conditions can affect future fertility — but most women go on to have healthy pregnancies. Emotional healing is just as important as physical recovery — counseling and support groups help. Talking about pregnancy loss reduces stigma — and empowers women to seek care and support. Essential Steps to Proactive Diagnosis and Care Both miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy are diagnosed through a combination of: Ultrasound to confirm the location and status of the pregnancy Blood tests to measure hCG (pregnancy hormone) levels Pelvic exams Treatment depends on the specific condition and severity: Miscarriage: May be managed expectantly (letting it pass naturally), medically (using medication like misoprostol), or surgically (e.g., D&C procedure). Ectopic pregnancy: Requires medication (like methotrexate) or surgery to remove the ectopic tissue and prevent complications. When Hope Hurts: Emotional Impact and Recovery Both miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy can be deeply traumatic. Feelings of grief, guilt, sadness, and even anger are normal. Healing is not just physical but emotional. Partners and loved ones may also experience emotional pain. Support and Coping Tips: Talk to your doctor about support groups or counseling Communicate openly with your partner and family Give yourself time to grieve and heal Consider speaking with a therapist or mental health professional Pregnancy loss — whether through miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy — is a deeply personal and often painful experience. If you or someone you love is going through this, know that you’re not alone. With proper medical care, emotional support, and time, healing is possible. Always seek professional guidance if you suspect anything unusual during pregnancy — early detection can save lives and guide better outcomes. Facebook Youtube Instagram Linkedin

The Ultimate Postpartum Care Guide- 6 Proven Tips for Postpartum Recovery & Self-Care
Discover everything about postpartum care, including recovery stages, symptoms, self-care tips, and common complications. Get expert advice on how to navigate the postpartum period smoothly.

Mental Health during Pregnancy- 7 Profound Tips
Mental health during pregnancy refers to a woman’s emotional, psychological, and social well-being before childbirth. It influences how she feels, thinks, and copes with pregnancy-related stress. Studies show that up to 1 in 5 women experience mental health issues during or after pregnancy, with depression and anxiety being the most common.
